
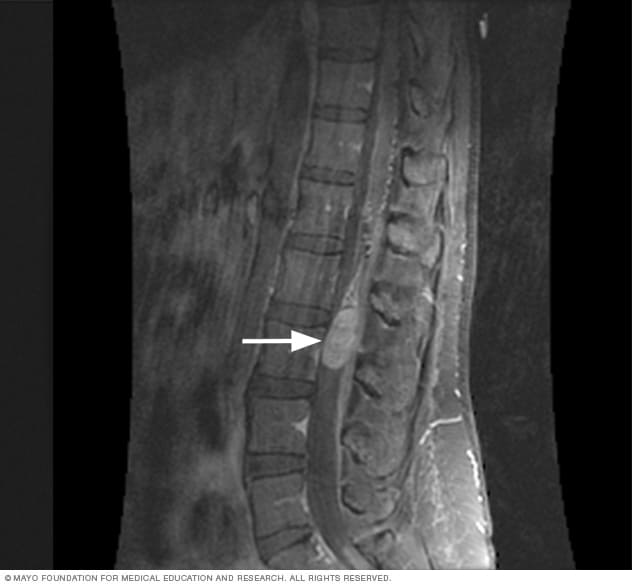
Artificial Disc Replacement/ Cervical Arthroplasty.Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF).Brain Aneurysm & Cerebrovascular Disease.During this procedure, the surgeon removes one or more samples through a surgical technique under general anesthesia. If a large tumor sample is required, the doctor may opt to perform a surgical biopsy. The procedure is typically performed with a local numbing agent (local anesthetic), although your doctor may have you sedated or under general anesthesia. The doctor extracts several small samples of the spinal tumor using a special type of hollow needle. There are two categories of biopsy: (1) needle and (2) surgical. Photo Source: biopsy may be performed to confirm the type of cancer. Imaging tests are necessary to identify specifics about the spinal tumor’s location, size, density and other characteristics. Most physicians opt for MRI and CT scans, which better define the tumor and its impact on the spine-even in the early stages. While an x-ray may initially be performed, it’s typically not the only imaging test, as x-ray won’t reveal spinal cord or nerve damage. CT and MRI studies may be performed with and without contrast. Imaging tests are necessary-such as x-rays, CT scans, and/or MRI-to identify specifics about the spinal tumor’s location, size, density and other characteristics. He/she may order additional lab tests to acquire a better understanding of your overall health too. If you’ve had previous tests (eg, blood work) performed by another specialist, your surgeon may need the results. Diagnostic StepsĪn in-depth physical and neurological examination and thorough review of your medical history is the first step. Together with you, a treatment plan is devised that addresses your diagnosis and symptoms. Your spinal cancer treatment team may include different medical specialists-such as your primary care physician, spine surgeon, medical oncologist, radiation oncologist, and interventional radiologist. Symptoms related to metastatic spinal cancer may be difficult to manage, but you don’t have to do it alone. The most serious cases of spinal cord compression may even cause death.įurthermore, a spinal metastasis may cause or contribute to vertebral compression fracture, or other structural changes in the spine that result in deformity, such as scoliosis.

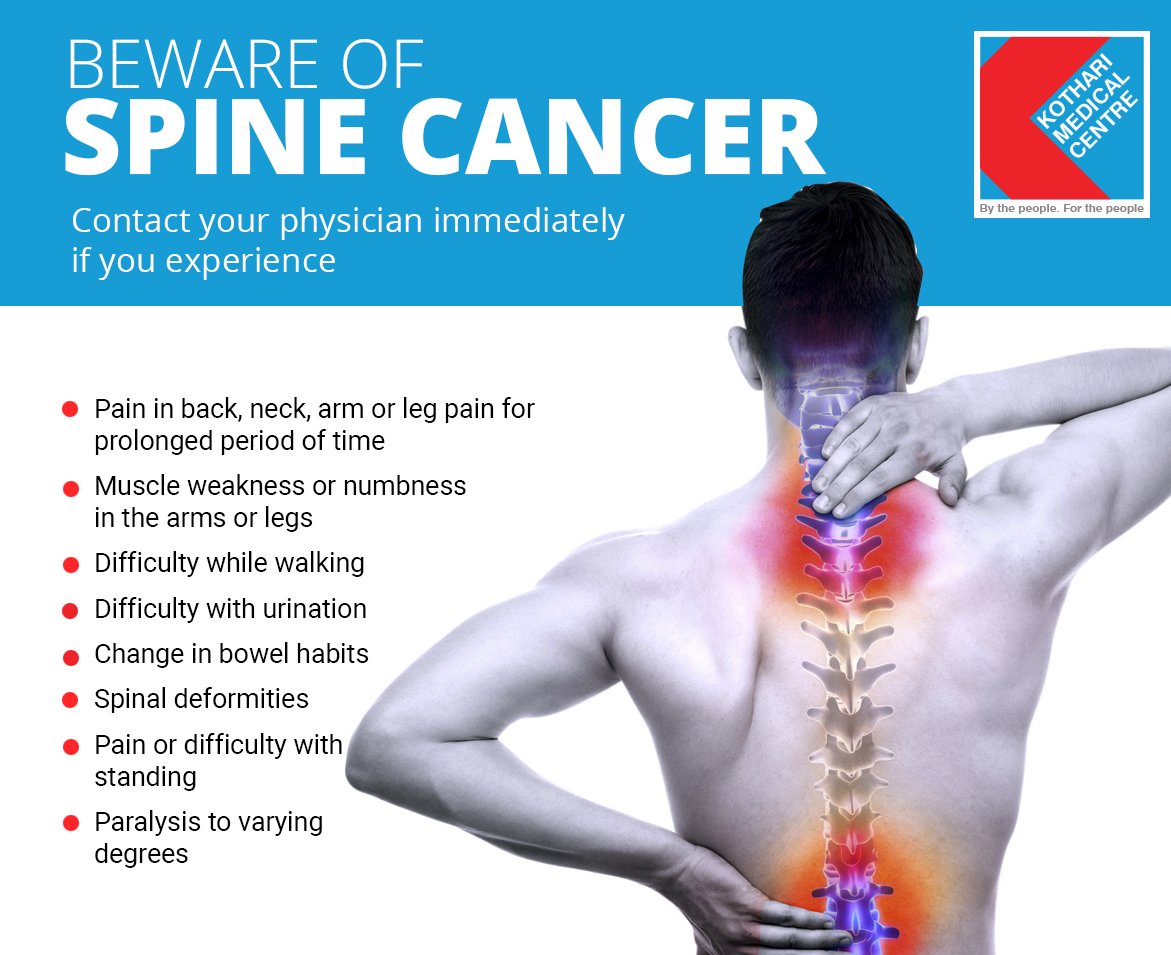
Spinal cord compression (eg, cervical myelopathy) may cause different neurological symptoms, including weakness, tingling, numbness, paralysis, difficulty walking, and loss of bowel/bladder control. In addition to pain, metastatic spinal tumors can compress your spinal cord. Many patients report the pain may worsen as their activity level increases and during the nighttime hours. Most people with a spinal metastasis experience pain in their mid-back or low-back regions, and it’s pain that seemingly has no cause (from an injury, for example). But, the first typical sign of a metastatic spinal tumor is back and/or neck pain, depending on the tumor's location in the spine. Back Pain Can be an Early Symptomĭepending on the size and location of the tumor, you may experience a range of symptoms. The spine is an integral part of the body's structural support, biomechanical functions and central and peripheral nervous systems. The tumor may impact spinal structures such as bones and nerves. Metastatic cancer that travels into your back and neck can cause significant symptoms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
